Intra- Operative Management and Nursing Care Using The Nursing Process
4. THE OPERATING TEAM
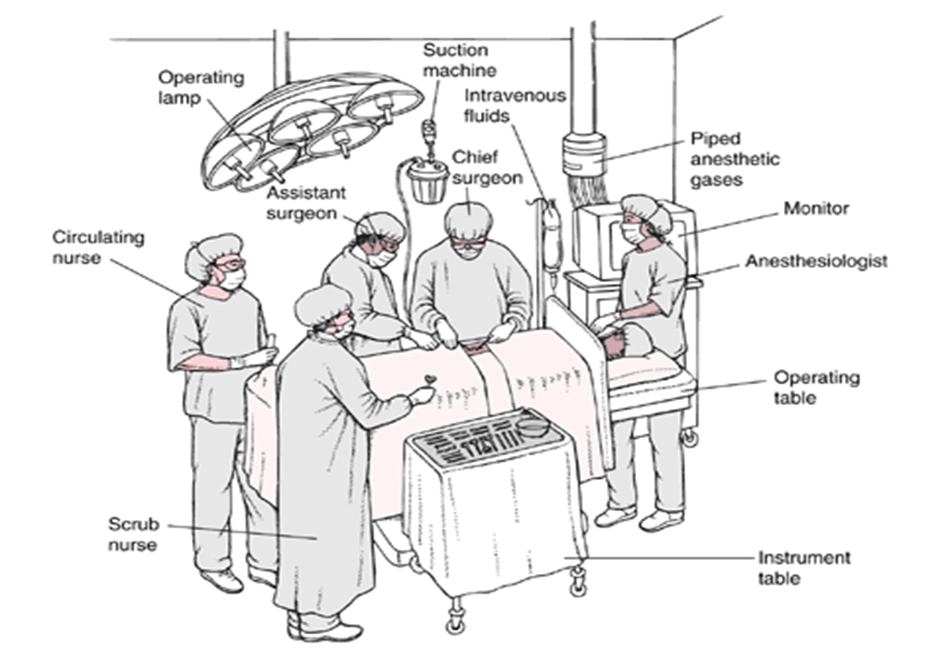
SURGICAL TEAM
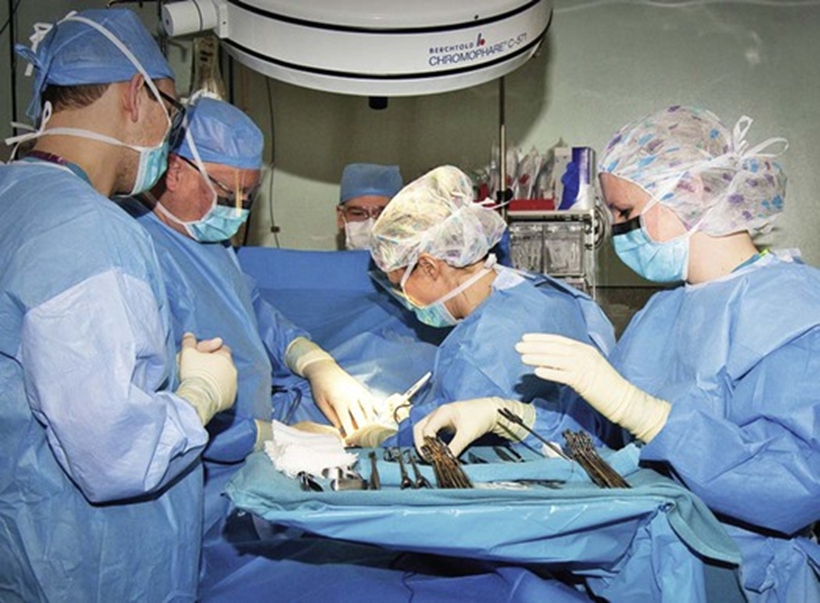
Surgeon
Surgeon heads the surgical team together with assistants, scrubs and performs the surgery.
Anesthesiologist or Nurse Anesthetist
Anesthesiologist or nurse anesthetist, administers the anesthetic agent and monitors the patient’s physical status throughout the surgery.
Registered Nurse
The perioperative nurse is a registered nurse (RN) who implements patient care during the perioperative period. Through close collaboration with the other members of the surgical team, you prepare the OR for patients before they arrive. You are usually the first member of the surgical team who meets the patient. You are the patient’s advocate throughout the intraoperative experience. This includes maintaining the patient’s safety, privacy, dignity, and confidentiality; communicating with the patient; and providing physical care. Assess the patient to determine any additional needs or tasks to complete before surgery. Provide physical and emotional comfort and patient and caregiver teaching regarding the upcoming surgery. In addition, work with the patient’s caregivers, keeping them informed and answering questions. This is particularly important in day-surgery areas where caregivers must assume greater responsibility for preoperative and postoperative care.In the perioperative role, you assume functions that involve either sterile or unsterile activities.
Scrub Nurse
When you serve in the role of scrub nurse, you follow the designated scrub procedure, are gowned and gloved in sterile attire, and remain in the sterile field. include performing a surgical hand scrub setting up the sterile tables preparing sutures, ligatures and special equipment (such as a laparoscope); assisting the surgeon and the surgical assistants during the procedure by: anticipating the instruments that will be required.
Circulating Nurse
When you serve in the role of circulating nurse,or circulator you remain in the unsterile field and so you are not gowned and gloved in sterile attire.Other task are:
- He or she manages the operating room protects the patient’s safety and health by monitoring the activities of the surgical team checking the operating room condition continually assessing the patient for signs of injury.
- Assisting with patient positioning.
- Preparing the patient’s skin for surgery.
- Managing surgical specimens, and documenting intraoperative events.
