Topic 2: Drug Control
LEARNING OUTCOMES
At the end of the topic, students should be able to;
1. Define the Poison and Control Substances.
2. Explain the Act of poison and Control Substances.
3. Explain the storage and proper documentation.
• Poison Ordinance / Dangerous Drugs
Controlled Substances Act: A federal law that regulates the prescribing and dispensing of psychoactive drugs, including narcotics, hallucinogens, depressants, and stimulants.
Dangerous Drugs Act 1952 (Act 234)
An Act to make further and better provision for the regulating of the importation, exportation, manufacture, sale, and use of opium and of certain other dangerous drugs and substances to make special provision relating to the jurisdiction of courts in respect of offences there under and their trial, and the purposes connected therewith.
The Controlled Substances Act is designed to remedy the escalating problem of drug abuse including:
- the promotion of drug education and research into the prevention and treatment of drug dependence
- the strengthening of enforcement authority
- the establishment of treatment and rehabilitation facilities
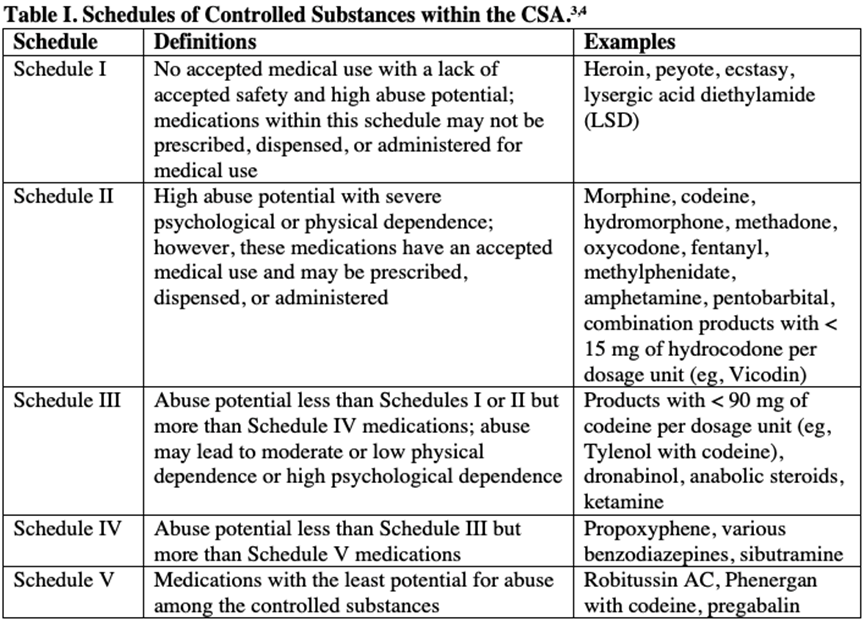
- the designation of schedules, or categories, for controlled substances according to abuse liability
Schedule Categories of Controlled Substances
Signs of drug Abuse
ü Problems remembering things you recently said or did
ü Getting drunk on a regular basis
ü Lying about how much alcohol you are drinking
ü Thinking that drug is necessary to have fun
ü Having frequent hangovers
ü Feeling run-down, depressed, or even suicidal
ü Having "blackouts"--forgetting what you did while drinking
ü Having problems at work or getting in trouble with the law
The Ten Most Dangerous Substances
1. Heroin - popular street names include smack, skag, and junk.
2. Cocaine - often referred to as snow, flake, coke, and blow.
3. Barbiturates - popular slang names include yellow jackets, reds, blues, Amy's, and rainbows.
4. Street Methadone
5. Alcohol
6. Ketamine - a powerful hallucinogen, often referred to as Special K.
7. Benzodiazepines - a family of sedative drugs.
8. Amphetamines - known as greenies among baseball players.
9. Tobacco
10. Buprenorphine
Other abused substances:
1. Cannabis - includes marijuana
2. Solvents - volatile substances that can be inhaled, such as glue, nail polish remover, paints, hair spray, and lighter fuel (gas).
3. 4-MTA - is a derivative of amphetamine and has similar effects to ecstasy.
4. LSD
5. Methylphenidate - central nervous system stimulant, commonly sold as Ritalin.
6. Anabolic steroids
7. GHB - short for Gamma hydroxybutyrate, a powerful central nervous system depressant, most commonly known as the date rape drug.
8. Ecstasy
9. Alkyl nitrates - group of drugs commonly referred to as poppers.
10. Khat - an amphetamine-like stimulant.
Goals in Handling Controlled Substances
1. To provide a controlled method for acquisition and dispensing of controlled substance.
2. To maintain appropriate proof of use
3. documentation in a retrievable manner.
4. To maintain a high level of security in the storage of controlled substances.
5. Nursing Interventions on Controlled Substances
6. Account for all controlled drugs.
7. Keep special controlled substances record for required information
8. Countersign all discarded or wasted medication.
9. Ensure that records and drugs on hand match
10. Keep all controlled drugs locked up, narcotics must be kept under double lock.
11. Be certain that only authorized persons have access to the keys.
• Documentations
All usage of controlled substances will be documented appropriately on the controlled substances documentation sheet or DDA book
DDA book consists of this following information:
· Date
· Name of client and RN
· Name of Dr ordering the controlled substance
· Signature of the nurse administering the medication
· Name of drug dosage form
· Amount given
· Balance on hand
In the event of an inaccurate count:
-Report immediately
-Remain on duty and search for missing narcotics
-Sign list as incorrect
-Fill out incident report and sign with one witness
If one part of a pre-measured dose of drug is given, a second nurse witnesses disposal of the unused portion and documents such on the DDA book
In some hospitals the empty ampule is required to be returned to the pharmacy
In the event of wastage or breakage of controlled substances, it must be documented in the DDA book
The nurse must state:
The date of event
Reason for wastage eg. Accidentally broken, expired or return to pharmacy
Amount wasted
Signature of the nurse wasting the substance
Signature of witness
• Storage
Dispensed to the ward using the stock supply or floor stock
Controlled substances must be stored under a double lock system
POISONS: Substance on which ingestion, inhalation, absorption, application, injection or development within the body, relatively small amount, may cause structural damage or functional disturbance
Poison a substance that if ingested even in very small amounts can harm or kill living things.
There are some substances that are considered poisonous even they are not classified as poison because they are dangerous only in relatively large amounts.
Toxicology is the study of poisons, how they work, their effects on the body, and the treatment of the conditions.
How Poison Works
Corrosive and irritant poisons like strong acids destroy or inflame the cells they contact.
Metabolic poisons like gases and drugs (that are toxic in overdose) act mainly by disrupting the body's chemical reactions.
Type of Poisons
Hydrocyanic (prussic) acid is one of the most rapidly acting toxins which affects mammals, this toxin acts in seconds.
Metallic compounds like mercury (commonly used in dental filling) and lead if ingested in small doses, may accumulate in the body for years before causing illness or death.
Botulinus toxin is the deadliest poison, it is secreted by a bacillus that causes food poisoning. It is deadly even in extremely small amounts.
Symptoms of Poisoning:
è Smell of poison on the breath
è Burning sensation in the throat.
è Vomiting and dizziness
è Poisoning may also be the cause if the person suddenly becomes ill, faint, and acts in a confused manner.
How to manage poisoning?
Check for signs and symptoms of poisoning. Some of the more common symptoms include:
§ Nausea and vomiting
§ Diarrhea
§ Abdominal pain
§ Burns or redness around the mouth
§ Unconsciousness, or slipping into unconsciousness
SELF-CHECK 2.1
1. Define Poison and Control Substances
2. How to do proper storage and documentation.