Topic 13: Generation of Biochemical Energy
TLO: Describe the importance of ATP as a source of energy.
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a macromolecule made of adenine, ribose and three phosphate group.
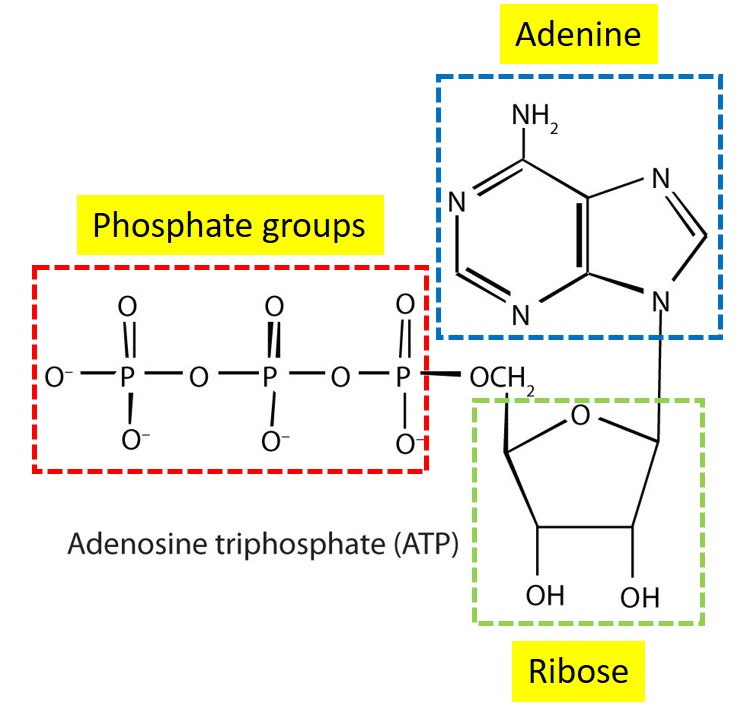
Figure 1 Structure of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). [Source: LibreTexts Chemistry]
The structural feature important in ATP is the phosphoric acid anhydride or pyrophosphate linkage. In the hydrolysis reaction, the pyrophosphate bond is hydrolysed when ATP is converted to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) that cause release of energy. Another reason for releasing energy is because hydrolysis process relieves the electron-electron repulsions experienced by the negatively charged phosphate group when they are bonded together.

Figure 2 ATP cycle and reaction coupling [Source: Khan Academy]
If hydrolysis of ATP releases energy, synthesis of ATP requires energy. Check out the hydrolysis and synthesis process of ATP down here:

Figure 3 Hydrolysis and synthesis of ATP.
Organisms use three mechanisms of phosphorylation to generate ATP:
1. Substrate-level phosphorylation generates ATP by transferring a high-energy phosphate group from an intermediate phosphorylated metabolic compound—a substrate—directly to ADP (Tortora & Derrickson, 2017). In human cells, this process occurs in the cytosol during glycolysis and Krebs cycle (refer to Figure 4). The substrate-level phosphorylation takes place both in the presence and absence of oxygen during glycolysis. However, in the Krebs cycle, it happens strictly in an aerobic environment.

Figure 4 The difference between substrate-level phosphorylation and oxidative phosphorylation. [Source: respirationresource.weebly.com]
2. Oxidative phosphorylation removes electrons from organic compounds and passes them through a series of electron acceptors, called the electron transport chain, to molecules of oxygen (O2) (Figure 4). This process occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane of cells (Tortora & Derrickson, 2017). Checkout the cool process of electron transfer throughout the inner membrane of a mitochondrion!
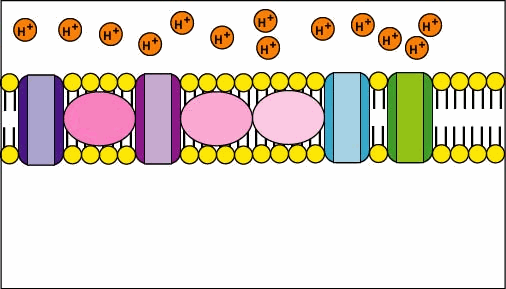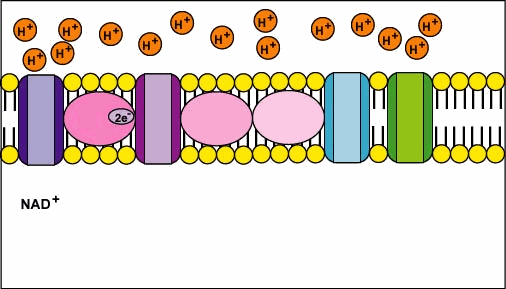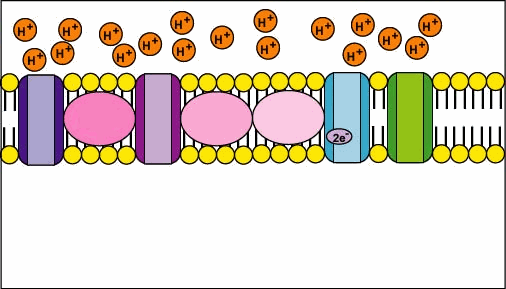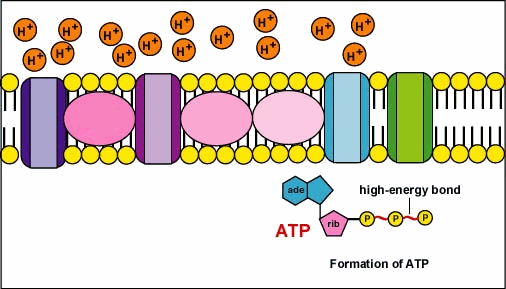
Figure 5 Electron transport chain [Source: faculty.ccbmd.edu]
3. Photophosphorylation occurs only in chlorophyll-containing plant cells or in certain bacteria that contain other light-absorbing pigments.
Learn more about ATP by clicking this video below: